Printf()
#Printf is a predefined function in "stdio.h" header file, by using this function, we can print the data or user defined message on console or monitor. While working with printf(), it can take any number of arguments but first argument must be within the double cotes (" ") and every argument should separated with comma ( , ) Within the double cotes, whatever we pass, it prints same, if any format specifies are there, then that copy the type of value. The scientific name of the monitor is called console.
Syntax
printf("user defined message");
Syntax
prinf("Format specifers",value1,value2,..);
Example of printf function
int a=10; double d=13.4; printf("%f%d",d,a);
scanf()
#scanf() is a predefined function in "stdio.h" header file. It can be used to read the input value from the keyword.
Syntax
scanf("format specifiers",&value1,&value2,.....);
Example of scanf function
int a; float b; scanf("%d%f",&a,&b);
In the above syntax format specifier is a special character in the C language used to specify the data type of value.
Format specifier:
| Format specifier | Type of value |
|---|---|
| %d | Integer |
| %f | Float |
| %lf | Double |
| %c | Single character |
| %s | String |
| %u | Unsigned int |
| %ld | Long int |
| %lf | Long double |
The address list represents the address of variables in which the value will be stored.
Example
int a; float b; scanf("%d%f",&a,&b);
In the above example scanf() is able to read two input values (both int and float value) and those are stored in a and b variable respectively.
Syntax
double d=17.8; char c; long int l; scanf("%c%lf%ld",&c&d&l);
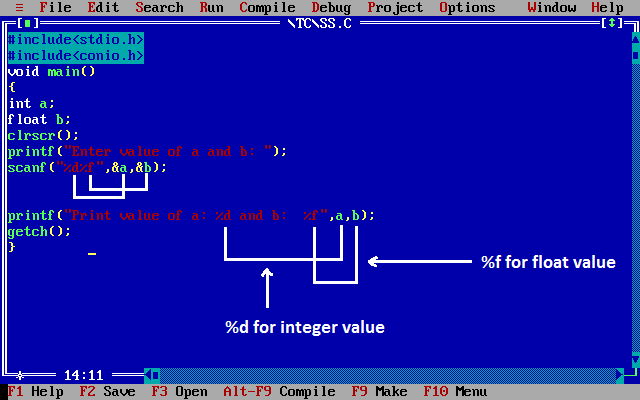
Example of printf() and scanf()
#include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main(); { int a; float b; clrscr(); printf("Enter any two numbers: "); scanf("%d %f",&a,&b); printf("%d %f",a,b); getch(); }
Output
Enter any two numbers: 10 3.5



