Storage Classes in C
#Storage class specifiers in C language tells to the compiler where to store a variable (Storage area of variable), how to store the variable, Scope of variable, Default value of a variable (if it is not initialized it), what is the initial value of the variable and life time of the variable.
Storage classes of C will provides following information to compiler.
- Storage area of variable
- Scope of variable that is in which block the variable is visible.
- Life time of a variable that is how long the variable will be there in active mode.
- Default value of a variable if it is not initialized it.
Type of Storage Class
Storage classes in mainly divided into four types,
- auto
- extern
- static
- register
Properties of All storage class
| Type | Storage place | Scope | Life | Default Value |
|---|
| auto | CPU Memory | body | Within the Function | Garbage value |
| static | CPU Memory | function | program | 0 (zero) |
| extern | CPU Memory | program | Till the end of the main program. | 0 (zero) |
| register | Register memory | body | Within the Function | Garbage value |
auto Storage Class
The auto storage class is the default storage class for all local variables. The scope auto variable is within the function. It is equivalent to local variable.
Syntax
{
int roll;
auto int roll;
}
In above example define two variable with same storage class auto and their scope is within the function.
Example of auto storage class
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void increment();
void main()
{
increment();
increment();
increment();
increment();
getch();
}
void increment()
{
auto int i = 0 ;
printf ( "%d", i ) ;
i++;
}
static Storage Class
The static storage class instructs the compiler to keep a local variable in existence during the life-time of the program instead of creating and destroying it each time it comes into and goes out of scope.
Example of static storage class
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void increment();
void main()
{
increment();
increment();
increment();
increment();
getch();
}
void increment()
{
static int i = 0 ;
printf ("%d", i ) ;
i++;
}
extern Storage Class
The extern storage class is used to give a reference of a global variable that is visible to ALL the program files. It is equivalent to global variable.
Example of extern storage class
Example
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int x = 20 ;
void main( )
{
extern int y;
printf("The value of x is %d \n",x);
printf("The value of y is %d",y);
getch();
}
int y=30;
Output
The value of x is 20
The value of y is 30
Register variable
Register variables are also local variables, but stored in register memory. Whereas, auto variables are stored in main CPU memory.
Advantages: The register variables are faster than remaining variables, because register variable are stored in register memory not in main memory..
Limitation: But, only limited variables can be used as register since register size is very low. (16 bits, 32 bits or 64 bits).
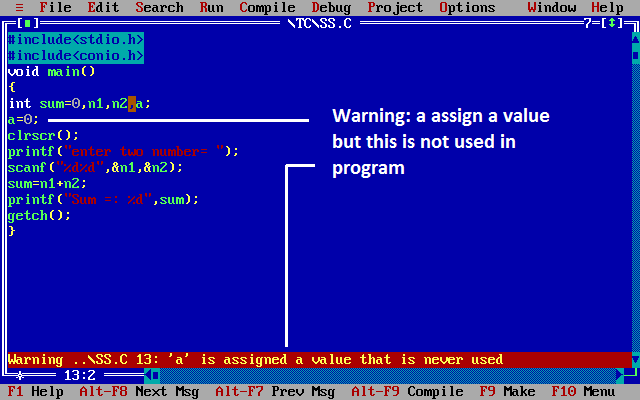
- In TC-3.0 we can't access the address of register variables.
- Pointer are ptr related concepts are can't applied to register variable.
Example
void main()
{
register int a=10;
++a;
printf("\n value of a: %d",a);
printf("Enter a value:");
scanf("%d",&a);
--a;
printf("\n value of a: %d",a);
getch();
}
Output
Input data is 50.
Error, must take address of a memory location.
Explanation
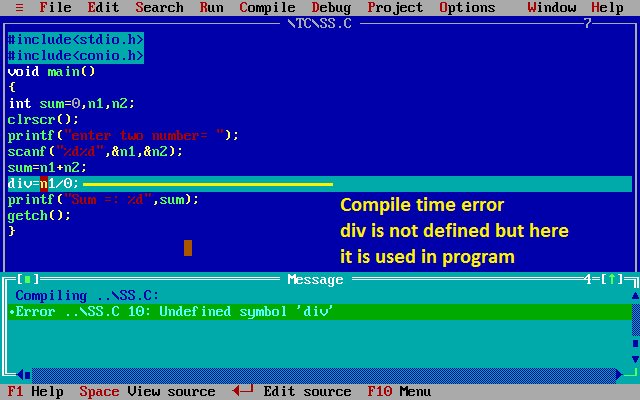
- In scanf() function if address is provided for the register variable then it will give error, if addition is not provided it normally work.
- Register storage class specifier just recommended to the compiler to hold the variable in CPU register if the memory is available or else stored in stack area of data segment.




Link list 2
Link list 1
Link list 3